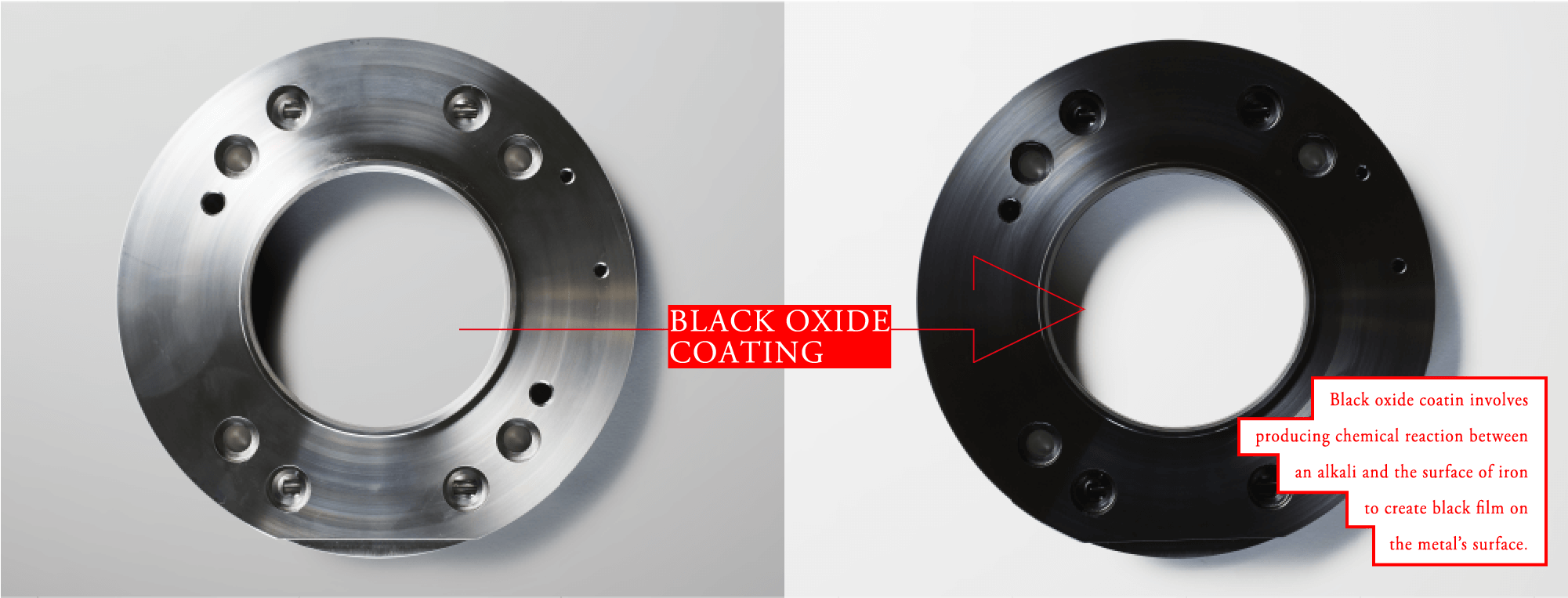
Electroplating is the process of applying one or more layers of a metal to a part by passing a positively charged electrical current through a solution containing dissolved metal ions (anode) and a negatively charged electrical current through your part to be plated (cathode).
Electroplating: A Proven Solution
The history dates back to the ancient Egyptians who would coat metals and non-metals with gold or a process known as “gilding”, the first known surface finish. Some metals apply more evenly than others, but the use of electricity means that the metal being deposited flows more easily to high current areas or the edges of a part. This tendency is especially pronounced on complex shapes or when trying to plate the inside or ID portion of a part.
Custom Electroplating Solutions Available
In addition to just single metals being applied, it is possible to simultaneously plate alloys of materials such as Tin and Lead or Zinc and Iron to achieve desired customized properties.

Types of Electroplating:
- Cadmium
- Copper
- Gold
- Hard Chrome
- Nickel
- Silver
- Tin
- Tin-Lead
- Zinc
- Zinc-Iron
- Black Nickel
- Black Chrome
Features of Electroplating:
- Corrosion resistance
- Wear Resistance
- Appearance
- Lubricity
- Solderability
Applications for Electroplating:
- Military weaponry
- Medical diagnostic instruments
- Optics
- Tools and dies
- Aircraft components
- Machine components
- Electronics & computer devices
- Enclosures, chassis and heat sinks
- Mechanical assemblies